How did Elon Musk grow his hair back? 6 Options
If you are currently reading this article, you’ve probably noticed that Elon’s hair has changed quite a lot and looks
The boom in genetic testing began when multiple test providers started combining their DNA genealogy packages with health packages. Sales data specifics aren’t available to the public, however, reports show that genealogy test sales more than doubled in 2017 with the total number exceeding 12 million sales. Some popular at-home genetic test providers are:
Genetic testing can be used as preventative screening for certain health reasons, understanding family heritage, and even for revealing genetic predispositions. Although genetic testing has its benefits, it’s important to be aware of the disadvantages as well.
Genetic testing looks at specific markers to determine a person’s risk of developing diseases. Getting a genetic test can help your doctor:
What exactly happens after a person submits their DNA sample?
DNA Is Analyzed: Computers put together all of the information that has been acquired up to this point and compares the DNA sample to a human reference genome. The lab will then get a report that lists any variants in the DNA.
Genetic testing is conducted in many ways and for many different reasons including:
Purchasing the top DNA test kits has increased in popularity because they are helping people feel more informed about their genetic makeup and giving them the results they’ve been waiting to hear, whether they be positive or negative. The reason behind why someone needs the kit will vary along with the results they’re looking for. Aside from providing their clients with answers, genetic testing has many benefits.
If you aren’t sure about where your family comes from, taking a DNA test might help. They often allow their users to learn about their ethnic background, where their family came from, and in some cases, different people from the past that they may be related to. Learning about your ethnic background can spark conversation about your family history and teaches you about your family’s past that you never knew.
Genetic predisposition is the increased chance of developing a disease or conditions due to the presence of one or more gene mutations and/or a family history that indicates an increased risk. This can cover everything from heart disease, to weight gain, or balding. However, even though it may be a genetic predisposition, preventing hair loss is possible. It is important to note that a predisposition is not an exact diagnosis, and that further testing may be done to better clarify results.
Genetic testing can help with the detection of disease within a person, both early on in life and later. In fact, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved DNA tests for 10 different diseases:
Even though genetic testing has multiple benefits, it’s important to be aware of the drawbacks that are bound to follow.
Genetic discrimination is when people are discriminated against based on their genetics. Some fear that when they participate in genetic testing this may happen to them. These fears might also persuade people not to participate in genetic studies or testing that is necessary to continue to develop new tests. The Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act was created in 2008 to prevent this from happening.
The most common question that is asked in regards to genetic testing is their accuracy. Since DNA test companies don’t release their data, scientists aren’t able to evaluate their accuracy and validate their testing methods. Experts are torn when it comes to believing the results — some do, and some don’t.
When you provide a company with your DNA you are providing them with your genetic code. Understandably, this can be nerve wracking. There have been a few cases of security breaches with big-name genetic test sites, resulting in millions of people having their identity and associated genetic data compromised. Some people also might question the security of their family’s secrets and whether or not someone else is able to steal their identity using their DNA.
If you are currently reading this article, you’ve probably noticed that Elon’s hair has changed quite a lot and looks

How Does Swimming Affect Your Body? Individuals swim for a variety of reasons including recreation, competition, and health. Regardless of

Lifestyle Tips For Better Overall Health The way you go about your daily life has a massive and direct impact
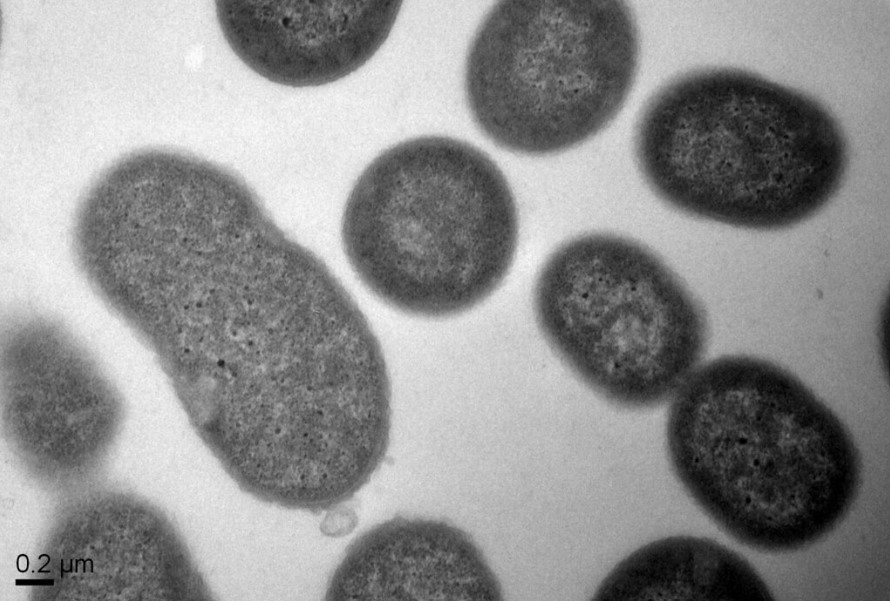
How Do Infections Work and What Are Their Effects on the Body? From Hippocrates’s writings about the spread of disease

How To Make a Good Impression in a Job Interview When it comes to getting a job, interviewing may seem